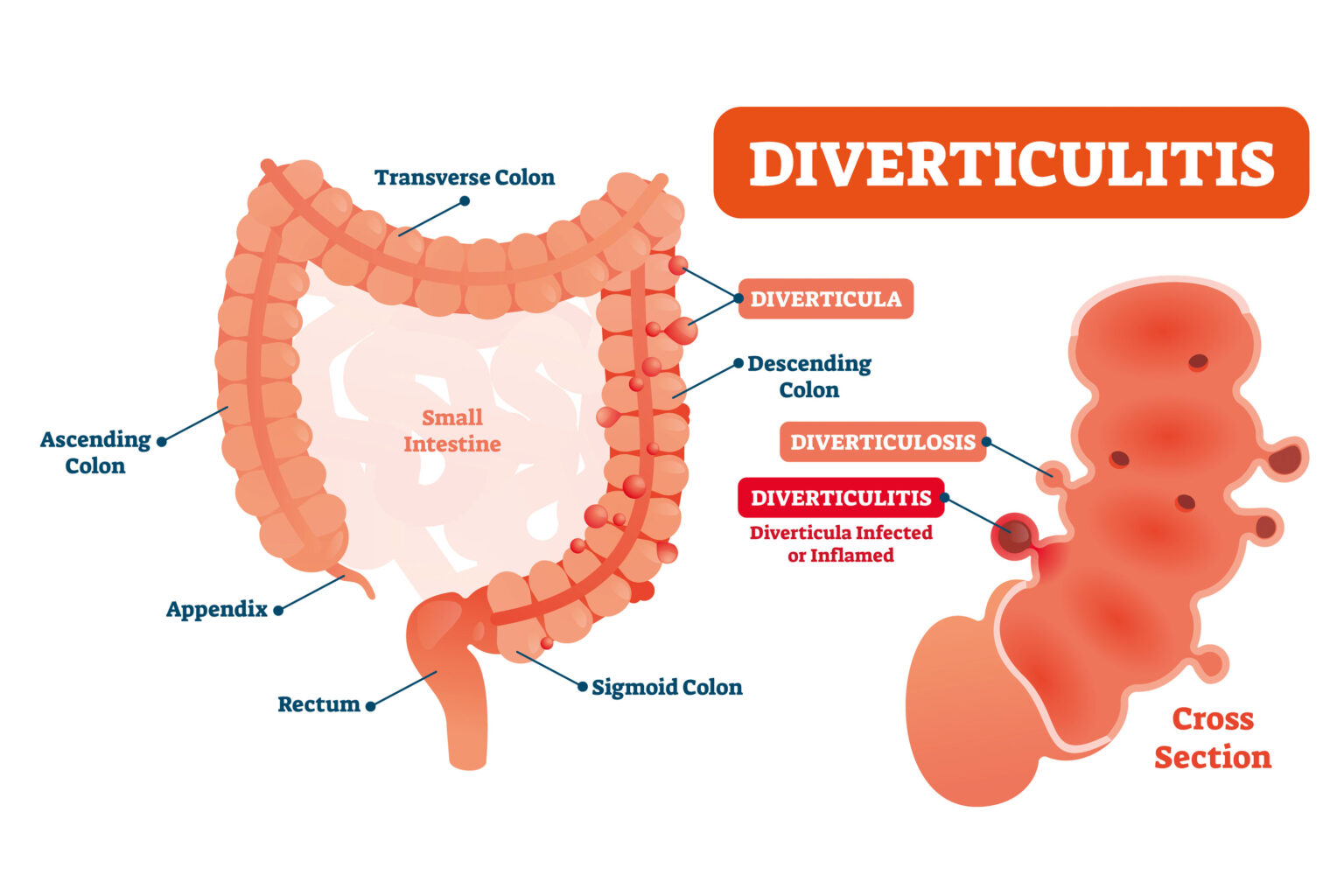
There are many changes that can occur within the digestive tract, particularly with age. One such change, which is increasingly common in patients over 40, is the development of small pouches within the digestive system’s lining, most often in the lower portion of the large intestine commonly referred to as the sigmoid colon. These bulging pouches are known as diverticula and their presence is a condition called diverticulosis or diverticular disease. In many cases, they cause no problematic symptoms. However, there are instances in which diverticulosis may progress into a condition known as diverticulitis.
What is diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis occurs when diverticula tear and become infected, inflamed, or both.
What are the symptoms of diverticulitis?
The most common symptom associated with diverticulitis is pain and tenderness in the lower left abdomen. This pain could be sudden and severe or mild and progressing in intensity over a course of several days. Additional symptoms of diverticulitis can include:
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation (diarrhea is less common)
- What are the complications of diverticulitis?
- Most patients with diverticulitis will not experience complications. However, about 25 percent could experience one or more of the following:
- Abscess in the colon wall
- Rectal bleeding
- Fistula, or abnormal tissue connection, between the bladder and colon
- Intestinal blockage from scarring
- Peritonitis, or abscess of the abdominal cavity which occurs when a perforation of diverticula allow contents of the intestine to seep out. Peritonitis is an emergency medical situation and could be fatal without prompt surgical intervention.
Who is Most Likely to Suffer from Diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is more likely to occur with age and is most often seen in those over 40 years old. Additional risk factors for developing the condition include:
- Being overweight
- Eating a diet that is low in fibre and high in animal fats
- Smoking
- Taking medications, such as prescription or over-the-counter painkillers
- Sedentary lifestyle
- How is diverticulitis treated?
Most cases of diverticulitis respond well to antibiotics. Additionally, a physician may recommend a temporary liquid diet as the colon heals. However, patients who have complications associated with diverticulitis may require additional interventions. These could include draining of an abscess or surgery in the most severe cases.
If you are suffering from the symptoms of diverticulitis, do not delay seeking treatment. With the appropriate course of antibiotics and dietary changes, it is likely that your case will resolve without complication. Contact your local GP and request an appointment with a specialist who will most likely carry out a Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy or CT scan.